The goal of this blog post is to introduce some of the concepts around artificial intelligence (AI), explain how they might be applied to retail and CPG now, and discuss what the future may hold. I’m going to be as succinct as possible and use as few buzzwords as I can in the explanations. The intent is not to let you win a bet around the bean-bag corral with your IT team but to provide a guide for where you might want to apply or learn about applying some of the more recent technology developments to your business.
Understanding AI
AI in its current form is anything that a machine does that seems intelligent to a human observer. This might be a robot shelf stocker or a plugin for your spreadsheet.
Machine learning is a subset of AI where computers learn from data without being explicitly programmed. For example, feeding 10 years of sales data into a machine learning model can help forecast performance at a new store or evaluate the impact of a new planogram.
What’s happening right now?
These AI capabilities are already in production and can offer a competitive edge.
Computer vision and image recognition
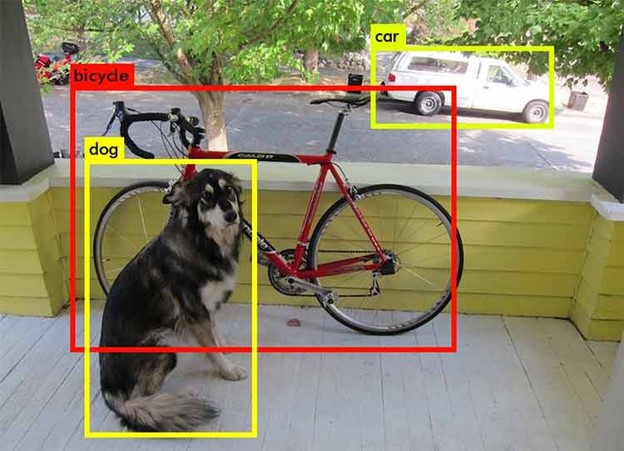
From share-of-shelf to detecting cancer, image recognition is visually engaging and functional. It works on both photos and video, offering benefits like detecting logos on social media or ensuring planogram compliance.
Image classification identifies overall concepts in an image using thousands of sample photos per category. It’s not suitable for counting but works well for tagging concepts.

Object detection identifies specific objects in images with bounding boxes and supports counting and spatial analysis.
Sentiment analysis
AI analyzes human sentiment in text. It can monitor consumer perception and flag significant comments for action.
- This soup is not like the usual garbage I hate. (positive)
- The salad tasted like it was supposed to be healthy. (negative)
- My friend said it was the best! (negative)
Predicting consumer interests
Recommendation engines power platforms like Amazon and Netflix. These tools are becoming increasingly accurate, helping businesses stock shelves or optimize packaging for specific audiences.
Natural language processing
NLP allows machines to understand and respond to human queries. It can handle common service requests efficiently, providing instant, personalized replies.
Examples include virtual assistants like Google Home and Alexa, not your old-school phone tree systems.
What’s happening in the future?
These innovations are emerging but not yet mainstream. Stay aware without investing too early.
- Self-driving cars: Major legal hurdles. More likely in internal logistics than open-road delivery—for now.
- Human-less stores: Amazon’s Go store is a headline grabber, but the cost and secrecy mean it’s not yet practical elsewhere.
- Walmart robots: Real-time shelf tracking is promising but limited by store complexity and cost.
- Drones: Cool but restricted by legal and regulatory requirements. Amazon is the leader here.